Nobel prize 2023 in medicine winners and their pioneering discoveries have reshaped the landscape of medicine by enabling the development of highly effective mRNA vaccines against COVID-19. This article explores their remarkable contributions to science and the global fight against the pandemic.
The Evolution of Vaccines
Vaccines before the pandemic
Traditionally, vaccines have relied on weakened or killed viruses to stimulate the immune system’s response. Max Theiler’s Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1951 recognized the development of the yellow fever vaccine as a pivotal achievement in this field. Subsequently, advancements in molecular biology led to the creation of vaccines based on specific viral components. For example, hepatitis B and human papillomavirus vaccines harnessed genetic information to trigger immune responses. Another approach used harmless carrier viruses, known as vectors, to deliver viral proteins and initiate immune reactions.
However, these methods were resource-intensive, dependent on large-scale cell culture, limiting their agility during outbreaks and pandemics.
The Rise of mRNA Vaccines
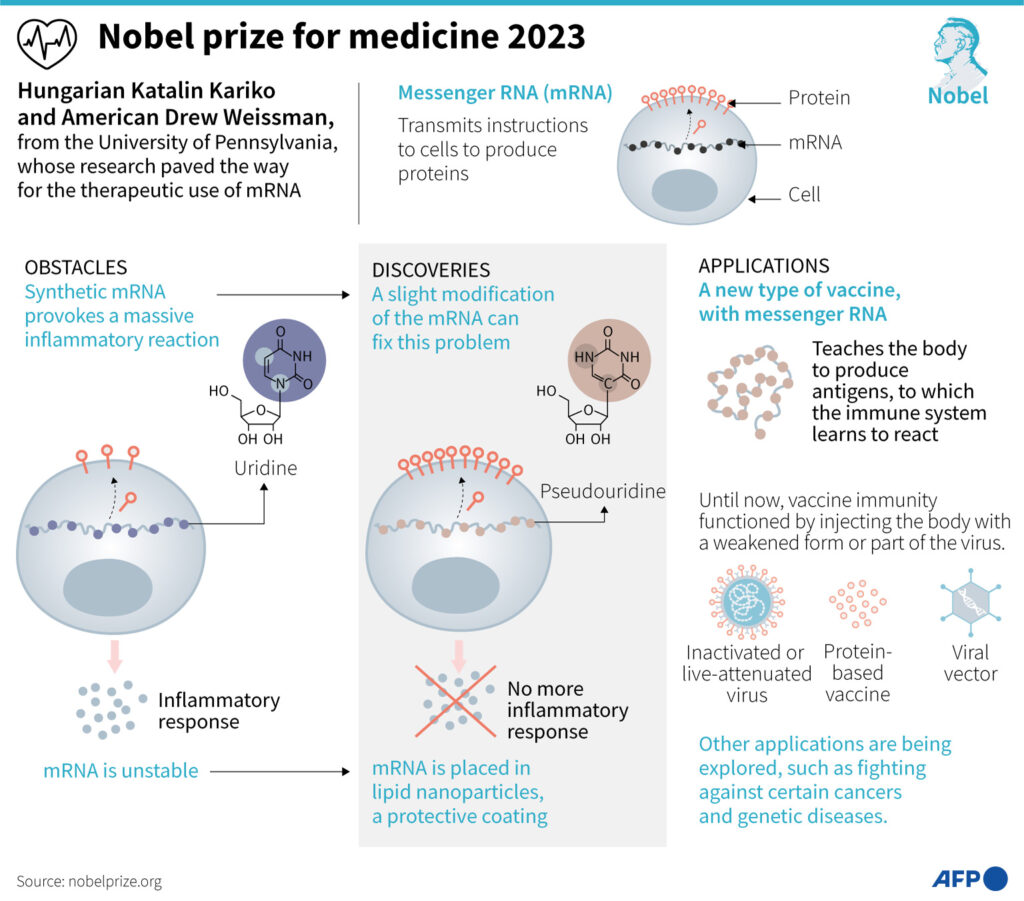
In the 1980s, a game-changing technology called in vitro transcription was introduced, allowing the production of mRNA without cell culture. While initially seen as unstable and challenging to deliver, it sparked the idea of using mRNA for vaccines and therapeutics. Katalin Karikó, a determined Hungarian biochemist, and immunologist Drew Weissman embarked on a journey to explore this concept further.
The Breakthrough Discovery
Karikó and Weissman’s collaboration revealed a pivotal insight – dendritic cells recognized in vitro transcribed mRNA as foreign, causing inflammatory reactions. To unravel this mystery, they examined the chemical makeup of RNA and discovered that the absence of altered bases in in vitro transcribed RNA triggered the unwanted response. They designed mRNA variants with unique chemical alterations, reducing inflammatory reactions significantly. This breakthrough, published in 2005, laid the foundation for the development of mRNA-based therapies.
Also read: futuristic serious impact of sleep apnea
Realizing the Potential
Subsequent studies by Karikó and Weissman in 2008 and 2010 showed that base modifications not only reduced inflammation but also enhanced protein production, eliminating major obstacles to mRNA clinical applications. Their discoveries paved the way for mRNA vaccines.
mRNA Vaccines
In 2020, the world faced a colossal health crisis with the outbreak of COVID-19. Thanks to Karikó and Weissman’s groundbreaking work, nucleoside base-modified mRNA vaccines against the virus were developed at an unprecedented speed. These vaccines, encoding the SARS-CoV-2 surface protein, demonstrated a remarkable protective efficacy of around 95%. By December 2020, they were approved for use.
A Bright Future for mRNA Technology
The agility and speed of mRNA vaccine development not only transformed the COVID-19 pandemic but also hold promise for combating other infectious diseases. Additionally, mRNA technology may soon be employed for delivering therapeutic proteins and treating various cancer types.
Conclusion
The Nobel laureates of 2023, Katalin Karikó and Drew Weissman, have made indelible contributions to medical science. Their pioneering work on mRNA vaccines revolutionized healthcare, providing humanity with a powerful tool to combat pandemics like COVID-19. Their discoveries, born out of dedication and determination, have truly changed the course of medicine.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do mRNA vaccines work?
mRNA vaccines work by introducing a small piece of genetic material, messenger RNA (mRNA), into the body, which instructs cells to produce a protein resembling a part of the target virus. This prompts the immune system to generate a response, including the production of antibodies, without causing the actual disease.
What makes mRNA vaccines different from traditional vaccines?
Traditional vaccines use weakened or inactivated forms of the virus, while mRNA vaccines use a small piece of genetic material to trigger an immune response. This allows for faster vaccine development and production.
How have mRNA vaccines impacted the fight against COVID-19?
mRNA vaccines have played a pivotal role in combating COVID-19, offering high efficacy and rapid development. They have saved millions of lives and allowed societies to return to normalcy.
What does the future hold for mRNA technology?
mRNA technology holds promise not only for vaccines but also for treating other diseases, including cancer. Its adaptability and speed make it a transformative tool in modern medicine.


2 thoughts on “Nobel prize 2023 in Medicine”